A Review of Public Participation in the Affairs of Protected Areas in Foreign Countries
-
摘要: 公众参与是保护地治理研究领域中的重要内容之一。以Web of Science数据库收录的国外保护地公众参与领域相关文献为基础,运用可视化软件Citespace 5.0.R7及系统综述的方法,从公众参与在国外保护地领域的研究缘起、研究概况、主要研究内容、研究评述、研究展望及对中国的启示5个方面进行了总结。研究发现,国外有关保护地公众参与的研究涉及较为广泛,无论是对具体案例的分析,还是对基础理论的探讨,研究开始深化和细化,研究方法趋于多样。同时,对目前研究中所显现出来的一些局限性进行了归纳分析。在此基础上,提出应完善保护地及国家公园公众参与的理论体系,实现研究结果的普适性运用;构建保护地及国家公园公众参与的整体机制;深化保护地及国家公园公众参与的研究方法;深化实践应用研究,增加可借鉴性;探索具有中国特色的保护地公众参与路径来指导保护地公众参与研究。Abstract: Public participation is an attempt by development partners to broadly consult and involve the public as to where projects should be situated. As bottom-up management, it is also a management strategy to increase public enthusiasm and initiative, which has become a key concept and common practice for management of protected areas across the world. So research on public participation has been a focus in the field of protected area governance. Based on the relevant academic publications collected from the Web of Science database, this paper synthesizes the research origins, profiles, contents, perspectives and research forecast by using the software Citespace 5. 0. R7 and systematic review methods. First, we investigate the general characteristics of these studies. This research shows that public participation was first introduced as a research topic in protected areas in the end of 20th century, then developed slowly in the early 21st, and the literatures emerged in large numbers after 2009. Most research has been carried out in United States, United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, Germany and so on, and these studies show an extension from nature conservation to ecosystem management, environmental change, environmental governance, and stakeholders related to protected areas, demonstrating a development process from a single problem to a multi-dimensional study. And most of the studies used qualitative methods. Second, we analyze the theoretical bases of all the papers and find that theoretical research mainly involves two aspects, one is to introduce other theories into the protected areas, such as stakeholder theory, governance theory, deliberative democracy theory and planned behavior theory; the other is to generalize the ideas embodied in public participation practice in protected areas and form a new theoretical framework. Third, we analyze the actual research content of these papers from four aspects. The first aspect is to analyze the values underlying public participation in protected area affairs. For this aspect, foreign researchers put forward the idea that effective public participation can not only balance the interests between the public and the government to achieve the dual value of the two, but also contribute to the sustainable development of each areas. The second aspect analyzes the limitations and shortcomings in public participation in protected areas. Some studies reveal that public participation can divide stakeholders, making it really difficult for any effective coalition of stakeholders to emerge, leaving out a large barrier-cost, diffuse citizen goodwill and so on. The third aspect is influencing factors of public participation. The fourth aspect is the evaluation of public participation. Fourth, we evaluate the status of international research and find that the papers involve a wide range of objectives. Whether it is the analysis of specific cases or the discussion of basic theories, it begins to deepen and refine, and the research methods tend to be diverse. But there are still some limitations emerged in the current research. In conclusion, the study suggests that future research should pay attention to the following matters: improving the theoretical system of public participation of protected areas and then realizing the universal application of research results, building the overall mechanism of public participation of protected areas; deepening the research methods and practical application research to increase reference, and exploring the paths of public participation of protected areas with Chinese characteristics.
-
Keywords:
- public participation /
- protected areas /
- affairs of protected areas
-
世界上第一个现代意义上的自然保护地诞生至今已有近150年的时间,作为保护和维护生物多样性、自然及文化遗产的重要形式,保护地的做法被各国广泛采用。在最初,很多国家建立及治理保护地,采用的都是自上而下的政府强制性管理模式。但在长久的实践中发现,该模式对资源保护的效果是失败的,出现了很多问题,如政府与当地社区的矛盾关系、政策与实践脱节等[1-2]。为了解决这些问题,兴起于20世纪60年代,并在西方新公共行政改革[3]及环境行政管理中取得显著成效的公众参与被引入保护地管理中。随着保护地管理领域不断扩大及公众参与的发展,一切与保护地有关的事务与活动,包括保护地的建立、规划、计划和治理,也包括与保护地相关的法律法规、政策的制定与实施,统称为保护地事务,都有公众的参与。公众参与已经成为实现保护地适应性管理的重要途径[2]。因此,公众参与已成为国外保护地一个重要的研究内容。
通过对国外公众参与保护地文献的梳理发现,国外研究已经涉及保护地公众参与的作用与意义、理论研究及实践研究等几个方面。在理论研究中,包括应用在公众参与方面的理论基础以及根据实践总结的理论框架;在实践研究中,包括公众参与前要明确的影响因素及限制条件,公众参与时选择适合的方式及途径,公众参与后的效果评估。
中国在保护地公众参与方面也进行了一些探索,《建立国家公园体制总体方案》中明确提出国家公园由国家确立并主导管理,需建立健全政府、企业、社会组织和公众共同参与国家公园保护管理的长效机制,探索社会力量参与自然资源管理和保护的新模式。到目前为止,国内的10个国家公园试点区中,在规划管理方面已有一些公众参与的实践,但仍处于较为浅显的层次,仍需继续深化。可见,探索我国公众参与保护地管理事务的理论体系与实践模式,已经成为一个具有重要价值的课题。鉴于此,本文将对国外公开发表的关于公众参与保护地事务研究的文献进行综述,进而提出中国以国家公园为主体的自然保护地公众参与的研究方向,为国内该领域的理论与实践提供借鉴。
一. 文献概况
一 文献数据来源
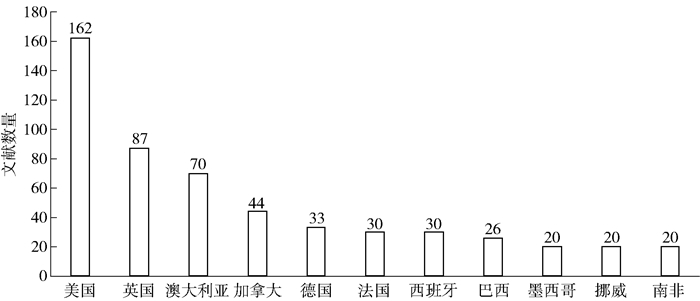
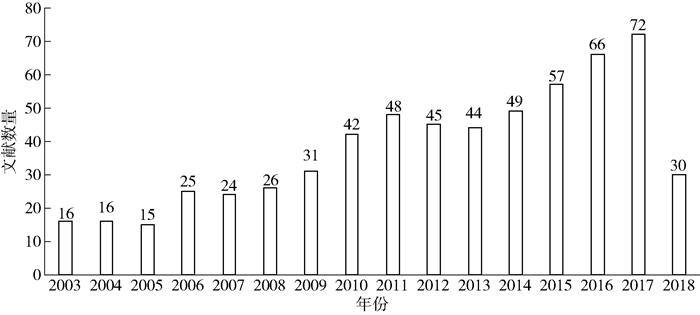
Web of Science(以下简称为WOS)收录了各个研究领域最具影响力的核心学术期刊,本文利用其为检索数据库,以主题“protected area”或“national park”和主题“participation”或“involvement”或“engagement”为条件,在1988—2018年的Web of Science核心集中进行检索,累计获得文献606条(截止到2018年5月28日)。文献类型包括研究论文(期刊、论文集、会议论文)、研究报告、书籍章节。在文献年度分布上,自21世纪初开始,国外对保护地及国家公园公众参与的研究逐渐关注,2009年之后,文献开始大量出现(见图 1,因1998—2003年之间的文献不符合要求,故本文从2003年开始统计)。发文靠前的国家依次为美国、英国、澳大利亚、加拿大、德国等(见图 2),其中美国占据绝对主导地位。美国作为世界上第一个建立国家公园这一类保护地的国家,在保护地公众参与方面积累了丰富经验,是很多国家和地区借鉴和研究的重点。
二 文献研究热点
文献的关键词是文章核心内容的浓缩和提炼,在某一领域文献中反复出现的关键词是该领域的研究热点[4]。在Citespace 5.0.R7中,高频度出现的关键词即为保护地和国家公园公众参与领域的研究热点(见表 1)。通过对研究文献进行关键词共现分析(见图 3)可看出,conversation(保护)、management(管理)和protected area(保护地)3个词的出现频次位于前列,说明公众参与在保护地管理和保护中具有重要作用,也被广泛应用于保护地的保护和管理中。2006年以后,研究热点向环境(environment)、治理(governance)、生态系统服务(ecosystem service)、影响(impact)、气候变化(climate change)、社区(community)等内容扩展,研究内容更加多样化。从关键词共现分析可以看出,公众参与在保护地领域的研究,呈现出从自然保护和管理、生物多样性保护逐渐向生态系统服务功能、环境变化、环境治理以及与保护地相关的利益相关者等内容延伸,是一个从单一问题到多维度研究的发展过程,研究内容越来越全面。
表 1 保护地及国家公园公众参与研究高频度关键词关键词 出现频率 中心性 年份 conversation 29 0.00 2003 management 18 0.00 2008 protected area 17 0.00 2004 marine protected area 16 0.00 2008 reserve 16 0.00 2008 biodiversity conversation 15 0.00 2004 biodiversity 12 0.00 2003 perception 11 0.00 2008 participation 10 0.00 2007 impact 10 0.00 2008 forest 9 0.00 2003 fishery 8 0.00 2008 governance 8 0.00 2010 climate change 8 0.00 2011 national park 8 0.00 2004 fisheries management 7 0.00 2011 ecosystem service 7 0.00 2007 deforestation 7 0.00 2011 community 6 0.00 2012 environment 5 0.00 2006 三 文献研究方法
对所得到的606条文献记录逐篇识别,最后识别出与保护地及国家公园公众参与主题相关的文献116篇,并对文中所用的研究方法进行分析(见表 2)。在116篇文献中,绝大部分文献采用定性研究的方法,说明定性研究在保护地及国家公园公众参与研究文献中占有主导地位。定性研究方法主要用于保护地及国家公园公众参与的作用、优缺点、各阶段特征、障碍、主体界定、效果评价及有效参与等方面,其中常用的研究方法有结构化访谈、田野调查法、案例分析、焦点小组、话语分析等,可见定性研究方法的多元现象。定量研究方法主要有问卷调查、GIS/RS技术、建模法及多元分析法,用于保护地及国家公园公众参与偏好、影响因素、有效性及效果评价中。随着时间的推移,保护地公众参与研究对象及研究内容将越来越多元化和复杂,定性与定量方法的结合也更加密切,但仍以定性为主,定量是为验证定性的结果,使研究更有科学性,如研究公众参与的偏好、效果及影响因素。
表 2 国外保护地及国家公园公众参与研究领域相关研究方法研究方法 代表文献 结构化访谈 Smith S等[5]、Alkan H等[6]、Andrea V等[7]、Apostolopoulou E等[8]、Nabin B等[9] 田野调查法 Kelboro G等[10] 定性描述 Ruata N N等[11] 定性研究方法 荟萃分析 Andrade G S M等[12]、Sterling E J等[13] 案例分析 Abidihabib M等[14]、Almany G R等[15]、Gaymer C F等[16]、Kovács E等[17] 焦点小组 Bockstael E等[18]、Fischer A等[19]、Kelboro G等[10] 话语分析 Petursson J G等[20] 问卷调查 Apostolopoulou E等[8]、Nabin B等[9] 定量方法 GIS、RS Baskent E Z等[21]、Brown G等[22] 建模法 Boumaour A等[23]、Li T H Y等[24] 多元分析法 Chen J L等[25]、Buono F等[26] 二. 主要研究内容
一 公众参与在保护地中的作用与意义
公众参与是为满足自上而下与自下而上结合的发展需求,而居于“政府集权”与“公众自治”两种治理方式之间的状态[3, 27]。相对于前者,公众参与能让公众取得话语权以及让政府得到公众的信任;对于后者,公众参与能使政府获得公众在保护地管理中的支持与帮助,缓解自身在财政、物力、人力等方面的限制。所以,公众参与在保护地事务中具有重要作用。
平衡公众与政府之间的利益,实现二者的双重价值。具体来说,Tuler S等强调以更加透明和包容的方式开展政策规划和决策活动,能缓解政府机构面临的越来越大的管理压力,公众参与既能增强公众对政府的信任,又能使政府更好地回应公众的需求[28]。Smith等进一步提出,公众参与能够弥补预期管理和实际管理状态之间越来越大的差距,缩减政府预算的同时且能保证保护地政策制定的有效性[5]。Almany G R等提出科学家、当地社区的参与,既可增加保护地研究能力及数据传输从而提高政府管理效率,又能发挥公众的价值[15]。有学者也开始将公众参与的作用拓展到保护地管理中,Mbile P等提到保护地成功管理离不开社区参与[29]。公众参与将公众的目标和需求纳入保护地管理,增加了决策制定的合法性,公众知识的整合能为决策提供重要信息,从而提高决策质量[30-32]。也有学者通过论述缺少公众参与所带来的问题,从而说明公众参与的重要性。如Kelboro G等分析了自上而下的国家倡导的保护方式与当地发展需求及区域利益不匹配,加深了政府与公众的矛盾,要求采用跨学科和自下而上的公众参与解决该问题[10]。
实现保护地可持续发展。公众参与对保护地及保护地中社会生态系统可持续发展具有极大作用[33]。Herbert R J H等进一步以无脊椎生物保护为例,论述了将公众纳入区域决策可减少负面环境影响,促进可持续发展[34]。Nagendra H等也以尼泊尔和洪都拉斯为例,验证了实施共同管理的参与式方法,使奇特旺皇家国家公园中的森林得到全面保护,发展起来的生态旅游也给当地社区带来了大量的收入,实现了可持续发展[35]。西班牙马德里地区的瓜达拉马山国家公园同样将利益相关者纳入森林管理决策过程中,森林管理也变得更加可持续[36]。Lange E等以英国峰区国家公园为例,更具体地说明了缺少利益相关者和他们意见的规划方案很难突破现状及解决问题,而有利益相关者的参与,并且经过反复的磋商和参与,制定景观和土地管理的长期愿景,能最大限度地提高生态、野生动物和景观的长期效益[37];将当地社区隔绝在外的决策,政府也不愿意推动更具包容性的环境治理方法,将会阻碍环境保护的发展[38]。此外,Islam G M N等还阐述了当地社区参与保护地管理和渔业监管是有效管理的重要因素,用户的参与对保护地治理有着显著贡献,对有效管理起着重要作用[39]。
二 公众参与保护地管理的理论研究
理论研究主要包括两大方面,一是将公众参与的模式和理念引入保护地管理领域中,提出新的理论观点和理论框架;二是对保护地管理中公众参与实践所体现出来的理念进行概括提炼。
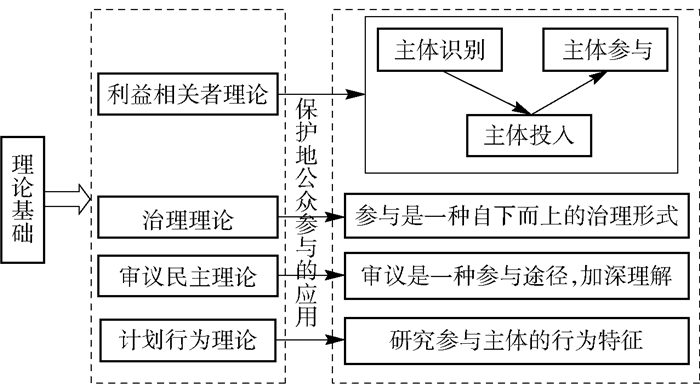
1.理论基础
主要理论包括利益相关者理论、治理理论、审议民主理论、计划行为理论(见图 4)。
1) 利益相关者理论。“利益相关者”一词在1963年作为一个明确的理论概念被提出,发展到目前已经形成了比较完善的理论框架。其被引入保护地管理研究领域,出现了大量基于此理论的实证研究,用于建立保护地公众参与管理计划。例如参与过程中的利益相关者识别、参与层次、参与的必要性及参与原则。具体如Masagca J等提出的SID-SIN-SEN方案(利益相关方识别(SID)-利益相关方投入(SIN)-利益相关方参与(SEN))为公众参与提供早期计划以保证计划的成功实施[40];Curzon R提出的利益相关者映射(stakeholder mapping)理论,从利益相关者的角度识别、分类及分析利益相关者的诉求从而实现其参与过程等[41]。
2) 治理理论。治理理论是使相互冲突的不同利益得以调和并采取联合行动的持续过程,核心是建立利益相关者之间的伙伴关系,保护地及国家公园公众参与属于保护地治理研究范畴。Bärner K提出,参与式保护作为自下而上的一种管理,是目前世界上最受欢迎的保护地管理模式[42];Hiwasaki L提出公众参与保护地相关政策决策是自下而上的治理形式[43]。
3) 审议民主理论。审议民主理论是20世纪后期在西方兴起的一种民主理论,认为民主不仅是投票和参与,在投票前应该有一个公共审议的过程,以深化公民对公共利益的理解,强调通过公共审议来提升参与品质。一些研究将其引入自然资源管理领域,例如Kovács E等提出民主理论对保护管理有效性有贡献[17],Rodela R认为审议民主观点在公众参与中的运用,有助于挑战自然资源管理中的一些既有传统,并导致开展和评估公众参与的新方式[44]。
4) 计划行为理论。计划行为理论是由Ajzen L提出的社会心理学理论,旨在描述人是如何改变自己的行为模式,主要被运用于研究微观个体在参与保护地管理过程中的影响因素。例如Ward C等以计划行为理论为基础,研究了马达加斯加保护地3个社区的参与情况,结果表明参与受到沟通不畅、缺乏谁可能参与以及如何参与的知识的限制[45]。
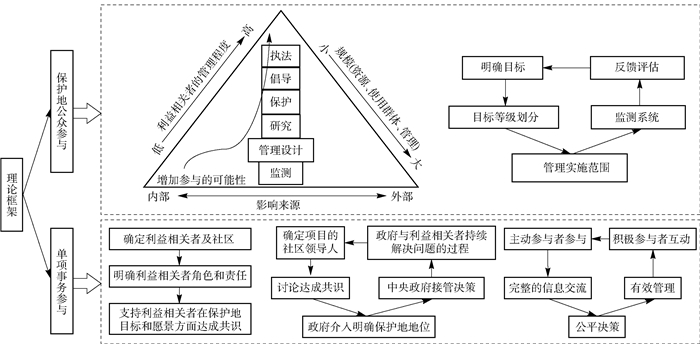
2.理论框架
学者根据个案研究,提出公众参与相关的理论框架,主要包括单项保护地的公众参与流程以及针对某项具体事务的公众参与流程(见图 5)。针对单项保护地的公众参与流程,Granek E F等通过对全球渔业管理案例分析,从影响来源、利益相关者管理程度及规模大小3个方面构建了渔民参与的框架,以期最大限度地提升参与项目成功的可能性[46]。Pollard S等以南非克鲁格国家公园河流管理为例,构建了基于利益相关者参与的框架,包括明确目标、目标等级划分、管理实施范围(包括确定参与主体、参与方式、参与范围)、监测系统、反馈评估过程与反馈循环5个方面,并将该框架推广到整个生态系统的管理[47]。
针对保护地某项具体事务的公众参与流程,Hiwasaki L以日本保护地资源保护为例,制定了利益相关者参与的自下而上的决策框架,从而建立一个超越政府边界并涉及当地社区的公园管理系统,具体包括确定公园管理中的利益相关者并确定社区;明确各利益相关者的角色和责任;支持利益相关者在保护地目标和长远愿景方面达成共识[43]。Rodríguez-Martínez R E同样制定了一个包含5个方面的社区参与保护地倡议的框架结构,包括确定项目的社区领导人、讨论达成共识、政府介入明确保护地地位、中央政府接管决策、政府与利益相关者之间持续解决问题的过程,该框架营造了合作共同管理的方式[48]。Dalton T M基于美国海洋保护地规划制定的过程,提出了影响公众成功参与的框架,具体包括5大方面:主动参与者参与、完整的信息交流、公平决策、有效管理和积极参与者之间的互动,该框架是对公众参与美国自然资源管理的实证和理论研究[49]。
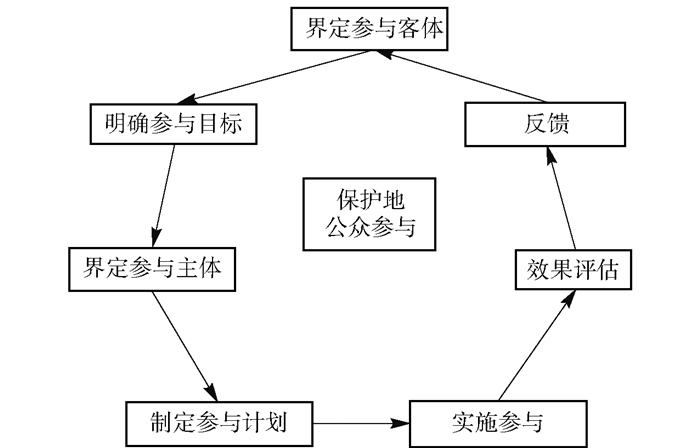
从学者的研究可以发现,不管是单项保护地亦或是某项具体事务的公众参与活动程序并未实现整体性构建,很多都是根据具体实践活动的性质而构建的,对同类型的推广有一定借鉴意义,但是否能推广到更广泛的领域,还值得进一步研究。不过前人的研究也积累了一定的基础,可以发现,保护地事务的参与流程包括界定参与客体、明确参与目标、界定参与主体、制定参与计划、实施参与、效果评估、反馈等7个步骤(见图 6)。
三 公众参与在保护地中的实践研究
依据保护地公众参与发生的过程,可以分为参与前、参与中和参与后。参与前,应该明确参与的限制条件及影响因素,尽最大可能排除各项因素对参与效果的影响;参与中,根据参与内容及参与主体,选择适合的方式及途径;参与后,需要对整个参与进行评估,了解参与效果及后续需要改进的地方,从而促进整个保护地公众参与的发展。
1.参与前,明确限制条件及影响因素
公众参与已经成为全球保护管理的一个关键概念,自20个世纪70年代以来,成为很多国家保护地及国家公园管理的常规做法,尽管绝大多数学者认为公众参与有助于成功的治理政策制定,并有助于建立参与式民主。然而,也有学者通过分析决策过程、决策结果、决策模式变化等公众参与保护事务的内容,得出公众参与保护地及国家公园治理存在的局限与缺点。也有学者相继关注并研究影响保护地公众参与的影响因素。在公众参与前,需要明确影响公众参与的因素以及这些限制条件,从而保证公众参与发挥其作用。
1) 公众参与的影响因素
国外关于公众参与保护地及国家公园影响因素的研究主要是从公众层面、综合性层面两个方面展开研究,其中综合性层面包括本身考虑因素的综合性及与其他学科理论结合的综合性。
基于公众层面,参与保护地事务的影响因素包括性别、时间、受教育程度、收入、对保护地的态度及看法、参与事务的偏好、参与事务的缺陷、各种技术和组织限制、对政府一些行为的感知。Nabin B等对尼泊尔的实证研究验证了性别、受教育程度、家庭富裕程度及对保护地所持态度是公众参与保护计划的重要影响因素[9];Heck N等[50]、Rodríguezizquierdo E[51]、Octeau等[52]基于具体参与项目的执行,得出缺乏时间和金钱、治理项目本身的缺陷以及各种技术和组织限制,如没有为公众提供足够的时间和信贷投入、参与项目晦涩难懂等都会对公众参与产生影响;Alkan H[6]、Daim M S[53]、Sirivongs K[54]等基于不同国家的实证案例研究发现,社区居民中对保护地事务持消极看法的居民一般不参与管理,持积极态度的居民才会参与;同样的,Fischer A等通过焦点小组讨论法验证了公众对保护地生物多样性管理的态度和认知是影响其参与决策过程的障碍,所以提高公众对保护地生物多样性的积极认知对设计公众支持的保护地生物多样性相关政策至关重要[19];了解当地居民对保护地保护工作的看法,可为实施参与式保护创造可行的长期战略[55]。Focacci M等通过对意大利南部的森林景观规划案例进行研究发现,公众对森林所提供的服务和产品的偏好会影响其参与,所以通过了解公众偏好,有利于确定参与的优先事项[56]。除此以外,政府的一些行为也会影响公众的参与,Niedziałkowski K等以波兰公众参与为例,得出政府行政能力不足或者缺乏对当地人的知识和兴趣,都会影响公众参与保护地管理的态度和行为[57]。
基于综合因素层面,Dalton T M认识到公众的主动参与、完整的信息交流、公平决策、有效管理、积极参与者之间的互动,以及包含这些因素的公众参与过程将更有利于产生得到公众支持的决策[49]。而且,公众对环境问题的认识、与政府之间的互动程度、村庄本身之间的差异都会对公众产生影响,需要制定适合特定地方群体的战略和举措,以优化公众在保护问题上的投入[42]。而在发展中国家,公众参与则存在更多的影响因素。Twichell J等通过对菲律宾民都洛岛和巴坦加斯省海洋保护地公众参与的研究发现,人口统计学特征、保护信念和科学正确的认识以及其他社会生态因素都会影响公众参与[58];Vodouhê F G等以贝宁的彭贾里国家公园为例,进一步提出4个方面的影响因素:是否有涉及当地社区的管理战略、公众的教育水平、保护的积极行为、公众效益认识[59];Ruizmallén I等以墨西哥社区为例,经过实证研究揭示了管理方式、外部资源支持的程度以及社区的社会组织都是影响公众参与的因素[60]。
此外,国外还有将心理学经典的理性行为理论——计划行为理论(Theory of Planned Behavior, 简称TPB)和传播学及营销学分析信息细化行为的理论动机-机会-能力理论(Motivation-Opportunity-Ability,简称为MOA)运用到公众参与的影响因素研究中,深入分析参与者的参与信念、参与态度、参与意向、参与动机、参与机会以及参与行为。Ward C等基于计划行为理论,以马达加斯加保护地3个社区为案例,分析了谁参与以及参与的原因、参与的预期收益和成本、社区内部如何分配成本和收益,结果表明社区参与受到沟通不畅、缺乏有关谁可能参与及如何参与的知识的限制[45]。而Rasoolimanesh S M等运用MOA模型调查了社区参与遗产保护地的影响因素,并得出各因素对3个社区参与程度的影响,调查结果显示,动机对低水平的社区参与具有最大的积极影响。机会对高水平的社区参与影响最大。在能力方面,即意识和知识方面,更多的知情居民对较低的社区参与程度感兴趣,而知识较多的居民对较高的社区参与程度更感兴趣[61]。
2) 公众参与的限制因素
对保护地公众参与影响因素的研究虽有一定进步,但很多因素并未给出影响的作用是积极或者消极,所以也有学者专门研究了保护地公众参与的限制因素。关于公众参与限制因素的研究,主要从政府角度、公众角度及参与事务本身3个方面进行。对政府来说,实施保护地事务的公众参与时间成本大,项目预算费用高,让决策失去控制,让参与的公众对其产生敌意;从公众层面来说,参与本身就是一个耗费时间的事情,而且本身的需求和身份也会随着参与事务而变化。甚至对公众来说,参与仅是既得利益者之间的权利游戏,忽略其他利益相关者,很难有合理的决策;对于参与事务本身,不管是不透明的决策,还是利益者分化,都使得参与难以实施或者让参与流于形式,让保护地治理变得效率低下[62-66]。这也说明,并不是保护地领域的所有事务都适合采用公众参与,学者也注意到保护地公众参与的适用条件及解决这些问题的方法。Niedzialkowski K等发现政府引导公众参与的能力的重要性。当政府在长期引导公众参与的能力有限时,并不能解决利益冲突,反而让参与成为利益相关者争夺权力的游戏[65]。Dietz等论述了当参与客体具有多维度、科学不确定的特征,利益相关者价值发生冲突或不确定,公众对管理机构缺乏信任等情况下,公众参与会是比较合适的选择[67]。
Hogg K等以西班牙东南部穆尔西亚省霍尔米加斯海洋保护地为例,针对利益相关者在参与保护地管理方面很难达成共识这一问题,通过分析利益相关者对参与决策价值的看法、参与的范围、参与的挑战以及克服这些挑战的方法,提出采用适应性共同管理的方法来解决该问题[68]。
2.参与中,选择适合的方式及途径
自参与式自下而上的保护地治理模式发展以来,各国依据自身国情探索出了适合本国保护地公众参与的多种参与方式,包括美国[69-70]、英国[37]、巴西[71]、澳大利亚[72]、加拿大[52]、日本[43]、尼泊尔[35]等(见表 3)。一些典型的公众参与方式包括信息公开、信息反馈、听证会、研讨会、讲习班等,也在越来越多的国家得到实践运用。从总体上看,不管是发达国家还是发展中国家,保护地事务中公众参与的内容离不开保护地的确立、规划决策、管理计划、环境影响评估等。基于这些参与内容选择的参与方式及参与途径也呈现多样化。此外,各国依据不同对象和目标也有一些典型做法值得推荐,包括成立咨询委员会,在参与事务之前,成立该委员会,囊括各利益相关者群体,促进公众的参与及公正性;通过合作伙伴关系,在保护地开展项目时,寻找当地社区、非政府组织、信托基金或者志愿者等公众主体合作,提高保护地的治理效果。
表 3 部分国家和地区保护地公众参与方式国家 参与内容 参与途径 典型做法 美国 保护地的确立、规划决策、管理运营、保护地范围界定、环评草案、环评决策 政府信息公开、公众信息反馈、互动交流、公开听证会、研讨会、开放日 合作学习、适应性管理、建立伙伴关系、成立咨询委员会 英国 参与决策、参与式规划方法 发起运动、研讨会 建立伙伴关系、成立信托机构和国家公园委员会 巴西 保护地的确立、保护地管理计划、特许经营计划 公众协商、研讨会 理事会与非政府组织共同管理、成立咨询委员会和社区居民协会 澳大利亚 保护地设立、管理计划制定 通知、咨询、协商 共同管理、合作,建立伙伴关系、公园之友 加拿大 保护地系统计划、计划目标制定、经营管理计划拟定 宣传会议、讲习班、调查表、意见听取会、研讨会 成立咨询委员会 日本 自然保护、保护地管理、环境影响评估、参与决策 发起运动、信息传播会议、书面评论、 成为合作伙伴 尼泊尔 特许经营 协商 共同管理 但是上述国家和地区保护地的公众参与方式主要是针对某一次具体的事务,只有一些基本的参与方式以及相应的手段,并没有形成具有层次以及成体系的参与方式,缺少从综合性视角对整个保护地领域公众参与方式的研究。基于此,通过对部分国家和地区公众参与方式的比较以及整合,可将保护地事务中的公众参与层次及方式总结为表 4。
表 4 保护地事务中的公众参与方式公众参与层次 公众参与方式 告知 政府信息公开,参加信息传播会议、宣传会议 咨询 参加公开听证会、研讨会、讲习班、意见听取会,成立咨询委员会 协作 合作学习,建立伙伴关系、信托机构、咨询委员会 公众自主 发起运动,成立社区居民委员会/协会 3.参与后,评估参与效果
在过去的几十年中,公众参与对保护地及国家公园的治理已经变得越来越重要了,所以评估保护地及国家公园公众参与的效果对了解过去的情况从而提高未来的参与质量至关重要[17]。Apostolopoulou E等以希腊保护地为实例验证了评估的重要性,尽管希腊保护地提出了将公众参与纳入保护地治理中,但是通过评估却发现,公众参与仍然存在于纸上,通过各级行政文件来规定的参与是空缺的,所以迫切需要通过制定和实施促进、参与指导培训等方式,形成公平、合作的双向参与式政策举措[8]。Bockstael E等进一步以巴西保护地为例,得出巴西现存的保护地参与式治理仅是参与的初始阶段,需要进行变革,才能实现自然资源管理的预期效果[18]。此外,学者开始分析世界各国案例,以评估公众参与的有效性,并找寻可推广的做法。Brown G等以挪威和芬兰为例,分析得出有效的公众参与需要根据不同国家的背景采取不同的策略[22]。Gaymer C F等进一步以世界各地的5个案例为研究对象,揭示了有效的参与需要持续时间的参与、参与的透明度以及能为社区带来福利,并且真正的参与需要授权参与,反过来要求加强教育和能力建设,从而让社区居民更好地参与保护地规划[16]。
也有学者做更深一步的研究,针对参与项目提出评估框架并进行评估或者与其他学科方法结合进行评估。如Sewell W R D等提出了公众参与项目评估框架和模型[73]。Kovács E等通过制定概念框架来评估参与式管理规划的过程和结果,并指出该评估框架适用于评估一整套与保护有关的管理规划过程[17]。Santana-Medina N等制定了评估公众参与有效性的指标,包括系统描述、可持续目标的确定、指标的选择及衡量可持续目标的进展[74]。Baskent E Z等通过GIS和RS的运用,得出只有在热心和熟练的利益相关者的参与下,参与才是有效的[21]。Li T H Y等与满意度测评结合,通过衡量利益相关者的满意度,提供了一种系统评价公众参与行为的有效性的手段[24]。Buono F等从社区居民的角度去评估公众参与保护地的效果,通过调查居民对管理机构最新管理理论的看法,认为最佳理论与实践之间存在差异,需要制定实用指南来指导公众参与[26]。
三. 研究评述
从国外保护地及国家公园中公众参与的研究历程来看,公众参与保护地事务的研究主题在不断增加,从保护、管理、保护地,再到治理、社区、环境等;与其他学科结合,研究领域也在逐渐扩充,其研究视角变得多元,从单纯的“保护中心主义”理念到逐渐重视各个参与主体参与的治理理念。
一 存在问题
从研究内容上看,由于世界各国在政治体制、文化价值、经济水平方面的差异,使得各国在公众参与保护地方面面临的问题以及解决方法既存在共性问题,也有个性化问题。目前关于保护地公众参与的文献主要侧重于个别案例研究或具体的地理环境,而对这些努力对保护结果的影响作出一般性结论非常困难,缺乏普适性[13]。公众参与作为一个复杂的社会问题,运用到保护地及国家公园,需要面对很多问题,如谁来参与、何时参与、参与什么、如何参与等一系列问题,这些单一问题又构成公众参与的整体性问题。但目前国外关于该领域的研究都是针对某一具体专题或者案例的研究,缺乏对参与的整体性考虑。
从研究区域来看,保护地及国家公园公众参与研究主要集中在美国、英国、澳大利亚、加拿大、德国、新西兰等保护地及国家公园公众参与开始较早的国家,其研究结论具有一定的可借鉴性,但是对公众参与发展并不成熟的国家和地区的关注较少。
从研究基础理论上看,该领域已经引入一些如利益相关者理论、治理理论、审议民主理论、计划行为理论等多学科理论,但是相对较为零散,尚未实现在该领域的有效整合。此外,现有提出的理论框架更多是根据公众参与实践所体现出来的理念进行概括提炼,缺乏更多的实践案例进行理论验证。
从研究方法体系上看,保护地及国家公园公众参与研究方法虽充分借鉴了多学科方法体系,但仍以定性研究为主,已有的定量研究及定性与定量相结合的研究多以经验数据对公众参与进行分析,对持续的公众参与演进的研究关注较少。
二 研究启示
国外在保护地及国家公园公众参与领域已取得一定的研究成果,但仍有一些方面需要继续加强和深化。在中国大力推进国家公园体制试点建设的大背景下,需要学习国外研究经验以及弥补我国的研究缺陷,具体需要从如下几方面来突破。
1) 完善保护地及国家公园公众参与的理论体系,实现研究结果的普适性运用。进一步借鉴社会学、公共管理等领域中的公众参与理论以及一些其他的新理论来丰富该领域的理论体系,并形成可推广、可借鉴的理论体系。
2) 构建保护地及国家公园公众参与的整体机制。针对公众参与的复杂性,借鉴其他研究领域,如环境保护领域中的公众参与,或新公共管理研究中的有效参与、决策模型,结合保护地特征,构建保护地公众参与整体机制。
3) 深化保护地及国家公园公众参与的研究方法及研究内容。在采用多学科方法的基础上,关注持续的公众参与的演进研究,经验数据研究可作为补充研究。对研究内容,不能单一从自然保护的角度出发,应结合中国具体国情,从生态系统服务功能角度出发的同时考虑人文生态系统。
4) 深化实践应用研究,增加可借鉴性。一方面运用国外实践总结出来的理论去检验更多实践案例,用于修正理论的同时也指导实践发展;另一方面总结国外成功案例,探索针对具体参与技术的实践指南。
5) 探索我国保护地及国家公园公众参与的具体路径。在考虑我国现有的政治制度、行政机制、文化背景等与西方国家的差异下,从我国保护地公众参与需注重公众参与意识提升,参与能力构建、提高,参与影响因素调查等方面,探索具有我国特色的公众参与保护地的实现机制。当然,关于公众参与的监测和评估也极为重要,针对每次的公众参与事务都应该进行评估与反馈,从实践中总结,从而上升为理论研究。
-
表 1 保护地及国家公园公众参与研究高频度关键词
关键词 出现频率 中心性 年份 conversation 29 0.00 2003 management 18 0.00 2008 protected area 17 0.00 2004 marine protected area 16 0.00 2008 reserve 16 0.00 2008 biodiversity conversation 15 0.00 2004 biodiversity 12 0.00 2003 perception 11 0.00 2008 participation 10 0.00 2007 impact 10 0.00 2008 forest 9 0.00 2003 fishery 8 0.00 2008 governance 8 0.00 2010 climate change 8 0.00 2011 national park 8 0.00 2004 fisheries management 7 0.00 2011 ecosystem service 7 0.00 2007 deforestation 7 0.00 2011 community 6 0.00 2012 environment 5 0.00 2006 表 2 国外保护地及国家公园公众参与研究领域相关研究方法
研究方法 代表文献 结构化访谈 Smith S等[5]、Alkan H等[6]、Andrea V等[7]、Apostolopoulou E等[8]、Nabin B等[9] 田野调查法 Kelboro G等[10] 定性描述 Ruata N N等[11] 定性研究方法 荟萃分析 Andrade G S M等[12]、Sterling E J等[13] 案例分析 Abidihabib M等[14]、Almany G R等[15]、Gaymer C F等[16]、Kovács E等[17] 焦点小组 Bockstael E等[18]、Fischer A等[19]、Kelboro G等[10] 话语分析 Petursson J G等[20] 问卷调查 Apostolopoulou E等[8]、Nabin B等[9] 定量方法 GIS、RS Baskent E Z等[21]、Brown G等[22] 建模法 Boumaour A等[23]、Li T H Y等[24] 多元分析法 Chen J L等[25]、Buono F等[26] 表 3 部分国家和地区保护地公众参与方式
国家 参与内容 参与途径 典型做法 美国 保护地的确立、规划决策、管理运营、保护地范围界定、环评草案、环评决策 政府信息公开、公众信息反馈、互动交流、公开听证会、研讨会、开放日 合作学习、适应性管理、建立伙伴关系、成立咨询委员会 英国 参与决策、参与式规划方法 发起运动、研讨会 建立伙伴关系、成立信托机构和国家公园委员会 巴西 保护地的确立、保护地管理计划、特许经营计划 公众协商、研讨会 理事会与非政府组织共同管理、成立咨询委员会和社区居民协会 澳大利亚 保护地设立、管理计划制定 通知、咨询、协商 共同管理、合作,建立伙伴关系、公园之友 加拿大 保护地系统计划、计划目标制定、经营管理计划拟定 宣传会议、讲习班、调查表、意见听取会、研讨会 成立咨询委员会 日本 自然保护、保护地管理、环境影响评估、参与决策 发起运动、信息传播会议、书面评论、 成为合作伙伴 尼泊尔 特许经营 协商 共同管理 表 4 保护地事务中的公众参与方式
公众参与层次 公众参与方式 告知 政府信息公开,参加信息传播会议、宣传会议 咨询 参加公开听证会、研讨会、讲习班、意见听取会,成立咨询委员会 协作 合作学习,建立伙伴关系、信托机构、咨询委员会 公众自主 发起运动,成立社区居民委员会/协会 -
[1] AGRAWAL A, GIBSON C. Enchantment and disenchantment: the role of community in natural resource conservation [J]. World Development, 1999, 27: 629-649. doi: 10.1016/S0305-750X(98)00161-2
[2] 张婧雅, 张玉钧.论国家公园建设的公众参与[J].生物多样性, 2017, 25(1): 80-87. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swdyx201701010 [3] 约翰·克莱顿·托马斯.公共决策中的公民参与: 公共管理者的新技能与新策略[M].孙柏瑛, 译.北京: 中国人民大学出版社, 2001: 3, 19, 33, 60. [4] 冯佳, 王克非, 刘霞.近二十年国际翻译学研究动态的科学知识图谱分析[J].外语电化教学, 2014(1): 11-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5795.2014.01.002 [5] SMITH S. Planning and management in Eastern Ontario's protected spaces: how do science and public participation guide policy?[EB/OL].[2018-09-20]. https://qspace.library.queensu.ca/handle/1974/7500.
[6] ALKAN H, KORKMAZ M, MCGILL D W, et al. Conflicts in benefits from sustainable natural resource management: two diverse examples from Turkey [J]. Journal of Environmental Biology, 2010, 31 (1-2):87-96. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6d42a3f6447d7cbf59b03e04eb8c0691&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[7] ANDREA V, ARABATZIS G, GEORGIOS T, et al. Administration and management effectiveness of protected areas: stakeholders' views of Dadia National Park, Greece[J]. Eco Mont-journal on Protected Mountain Areas Research, 2013, 5(2): 19-30. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Veronika_Andrea/publication/261319128_Administration_and_management_effectiveness_of_protected_areas_stakeholders%27_views_of_Dadia_National_Park_Greece/links/02e7e533d8c09f11aa000000.pdf
[8] APOSTOLOPOULOU E, DRAKOU E G, PEDIADITI K.Participation in the management of Greek Natura 2000 sites: Evidence from a cross-level analysis [J].Journal of Environmental Management, 2012, 113(52): 308-318. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8c64c0c51282e975b8d2540445c1b257&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[9] NABIN B, JOEL T. Heinen decentralization and people's participation in conservation: a comparative study from the Western Terai of Nepal [J].International Journal of Sustainable Developme $ World Ecology, 2007, 14(5):520-531. doi: 10.1080/13504500709469751
[10] KELBORO G, STELLMACHER T. Protected areas as contested spaces: Nech Sar National Park, Ethiopia, between 'local people', the state, and NGO engagement [J]. Environmental Development, 2015, 16:63-75. doi: 10.1016/j.envdev.2015.06.005
[11] RUATA N N, INDAR Y N, NIARTININGSIH A. The public participation against sustainability mangrove protection area[D]. Makassar: Universitas Hasanuddin, 2014.
[12] ANDRADE G S M, RHODES J R. Protected areas and local communities: an inevitable partnership toward successful conservation strategies[J]. Ecology & Society, 2012, 17(4):1-16. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_08126f5be77f7337598889735d9a31be
[13] STERLING E J, BETLEY E, SIGOUIN A, et al. Assessing the evidence for stakeholder engagement in biodiversity conservation [J]. Biological Conservation, 2017, 209:159-171. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2017.02.008
[14] ABIDIHABIB M, LAWRENCE A. Revolt and remember: how the shimshal nature trust develops and sustains social ecological resilience in Northern Pakistan [J]. Ecology & Society, 2007, 12 (2):375-386. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_97e334269cc0b7ec8b5b9f438f81ee17
[15] ALMANY G R, HAMILTON R J, WILLIAMSON D H, et al. Research partnerships with local communities: two case studies from Papua New Guinea and Australia [J]. Coral Reefs, 2010, 29(3):567-576. doi: 10.1007/s00338-010-0624-3
[16] GAYMER C F, STADEL A V, BAN N C, et al. Merging top-down and bottom-up approaches in marine protected areas planning: experiences from around the globe [J]. Aquatic Conservation Marine & Freshwater Ecosystem, 2015, 24(S2):128-144. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1d2e08fc796096af898b5f1cc439fd79&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[17] KOVÁCS E, KELEMEN E, KISS G, et al. Evaluation of participatory planning: lessons from Hungarian Natura 2000 management planning processes [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 204(1):540-550. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d261bd34be2aa5047963f59d34fb7bb1&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[18] BOCKSTAEL E, BAHIA N C F, SEIXAS C S, et al. Participation in protected area management planning in coastal Brazil[J]. Environmental Science & Policy, 2016, 60:1-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ff7a1e6cd125d3de24f76f53a27c0503
[19] FISCHER A, YOUNG J C. Understanding mental constructs of biodiversity: implications for biodiversity management and conservation [J]. Biological Conservation, 2007, 136 (2):271-282. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2006.11.024
[20] PETURSSON J G, VEDELD P. Rhetoric and reality in protected area governance: institutional change under different conservation discourses in Mount Elgon National Park, Uganda[J]. Ecological Economics, 2017, 131:166-177. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2016.08.028
[21] BASKENT E Z, TERZIOǦLU S, BAŞKAYA S. Developing and implementing multiple-use forest management planning in Turkey [J]. Environmental Management, 2008, 42(1):37-48. doi: 10.1007/s00267-008-9106-6
[22] BROWN G, HAUSNER V H, GRODZIŃSKA-JURCZAK M, et al. Cross-cultural values and management preferences in protected areas of Norway and Poland [J]. Journal for Nature Conservation, 2015, 28:89-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jnc.2015.09.006
[23] BOUMAOUR A, GRIMES S, BRIGAND L, et al. Integration process and stakeholders' interactions analysis around a protection project: case of the national park of Gouraya, Algeria (South-western Mediterranean)[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2018, 153:215-230. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2bf796f2e2a83a775d97cbd6cf15d15b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[24] LI T H Y, ST N G, SKITMORE M. Evaluating stakeholder satisfaction during public participation in major infrastructure and construction projects: a fuzzy approach[J]. Automation in Construction, 2013, 29 (1):123-135. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f9d5c19bc36b52055f49ba78848c2231&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[25] CHEN J L, LIU H H, CHUANG C T, et al. The factors affecting stakeholders' acceptance of offshore wind farms along the western coast of Taiwan: evidence from stakeholders' perceptions[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2015, 109:40-50. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5ab95046531672fd853360589e9bca02&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[26] BUONO F, PEDIADITI K, GERRIT J. Local community participation in Italian National Parks management: theory versus practice[J]. Journal of Environmental Policy & Planning, 2012, 14 (2):189-208. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=88f72f856a8ce532e1bd5db22aa740ce&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[27] 王京传, 李天元.国外公众参与旅游目的地公共事务研究综述[J].旅游学刊, 2014, 29(3):116-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5006.2014.03.013 [28] TULER S, WEBLER T. Public participation- relevance and application in the national park service[J]. Park Science, 2000, 20(1):24, 26, 47. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5399d4c627f0b9c2b2afb1cd9ea13a38&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[29] MBILE P, VABI M, MEBOKA M, et al. Linking management and livelihood in environmental conservation: case of the Korup National Park, Cameroon[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2005, 76 (1):1-13. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4b37a6e8404e63fb1adc32020ac0b365&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[30] LANGEMEYER J, PALOMO I, BARAIBAR S, et al. Participatory multi-criteria decision aid: operationalizing an integrated assessment of ecosystem services[J]. Ecosystem Services, 2018, 30:49-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2018.01.012
[31] MARKS R. Stakeholder participation for environmental management: a literature review[J]. Biological Conservation, 2008, 141 (10):2417-2431. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2008.07.014
[32] KAI M, KISHIDA S, SAKAI K. Applying adaptive management in resource use in South African national parks: a case study approach[J]. Koedoe - African Protected Area Conservation and Science, 2011, 53 (53):144-157. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_aa79e76a4b38c9ab4fa35e4aef9b6cf1
[33] MICHELI F, NICCOLINI F. Achieving success under pressure in the conservation of intensely used coastal areas [J]. Ecology & Society, 2013, 18 (4):59-63. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Doaj000003727495
[34] HERBERT R J H, HUMPHREYS J, DAVIES C, J, et al. Ecological impacts of non-native Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) and management measures for protected areas in Europe [J]. Biodiversity & Conservation, 2016, 25(14):1-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e8a29780de86c659ce8e8652c09ae635
[35] NAGENDRA H, TUCKER C, CARLSON L, et al. Monitoring parks through remote sensing: studies in Nepal and Honduras [J].Environmental Management, 2004, 34 (5):748. doi: 10.1007/s00267-004-0028-7
[36] MARTÃ-N-FERNÃ S, MARTINEZ-FALERO E. Sustainability assessment in forest management based on individual preferences [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 206:482-489. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bf5f6b6c14ae1cb899a6abd998d81ff9
[37] LANGE E, HEHL-LANGE S. Citizen participation in the conservation and use of rural landscapes in Britain: the Alport Valley case study [J]. Landscape & Ecological Engineering, 2011, 7 (2):223-230. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6e304a57e06c14b563c6fdaea7582f03&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[38] STRINGER L C, PAAVOLA J. Participation in environmental conservation and protected area management in Romania: a review of three case studies [J]. Environmental Conservation, 2013, 40 (2):138-146. doi: 10.1017/S0376892913000039
[39] ISLAM G M N, TAI S Y, KUSAIRI M N, et al. Community perspectives of governance for effective management of marine protected areas in Malaysia [J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2017, 135:34-42. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=63698877e6a50228e9b1077e41b9991a
[40] MASAGCA J, MORALES M, ARAOJO A. Formulating an early stakeholder involvement plan for marine protected areas (MPA) in Catanduanes Island, Philippines[J]. Turkish Journal of Fisheries & Aquatic Sciences, 2018, 18(1):131-142. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=81e7e57d09d2d51ba96b15e702b18e54&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[41] CURZON R. Stakeholder mapping for the governance of biosecurity: a literature review[J]. Journal of Integrative Environmental Sciences, 2015, 12(1):15-38. doi: 10.1080/1943815X.2014.975723
[42] BÄRNER K.Introduction of participatory conservation in Iran: case study of the rural communities' perspectives in Khojir National Park[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research, 2014, 8(4):913-930. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=659291ecbbe1c5ddf5cd04a0591d690e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[43] HIWASAKI L. Toward sustainable management of national parks in Japan: securing local community and stakeholder participation[J]. Environmental Management, 2005, 35(6):753-764. doi: 10.1007/s00267-004-0134-6
[44] RODELA R. Advancing the deliberative turn in natural resource management: an analysis of discourses on the use of local resources[J].Journal of Environmental Management, 2012, 96(1):26-34. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a6466dc46497acdf46616e3488b3cf77&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[45] WARD C, HOLMES G, STRINGER L. Perceived barriers to and drivers of community participation in protected-area governance[J]. Conservation Biology the Journal of the Society for Conversation Biology, 2017, 32(2):437-446. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28833471
[46] GRANEK E F, MADIN E M P, BROWN M A, et al. Engaging recreational fishers in management and conservation: global case studies[J].Conservation Biology, 2010, 22(5):1125-1134. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=423c2e0e3623275bfd9b29fc6658de15&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[47] POLLARD S, TOIT D D, BIGGS H. River management under transformation: the emergence of strategic adaptive management of river systems in the Kruger National Park[J]. Koedoe African Protected Area Conservation & Science, 2011, 53(2):1-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_4540a7b5cb0d0e0f3492686be06b947b
[48] RODRÍGUEZ-MARTÍNEZ R E. Community involvement in marine protected areas: the case of Puerto Morelos reef, Mexico[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2008, 88(4):1151-1160. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.06.008
[49] DALTON T M. Beyond biogeography: a framework for involving the public in planning of U.S. marine protected areas[J]. Conservation Biology, 2010, 19 (5):1392-1401. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/227523953_Beyond_Biogeography_a_Framework_for_Involving_the_Public_in_Planning_of_US_Marine_Protected_Areas
[50] HECK N, DEARDEN P, MCDONALD A, et al. Stakeholder opinions on the assessment of MPA effectiveness and their interests to participate at Pacific Rim National Park Reserve, Canada [J]. Environmental Management, 2011, 47 (4):603-616. doi: 10.1007/s00267-010-9609-9
[51] RODRÍGUEZIZQUIERDO E, GAVIN M C, MACEDOBRAVO M O. Barriers and triggers to community participation across different stages of conservation management [J]. Environmental Conservation, 2010, 37(3):239-249. doi: 10.1017/S0376892910000500
[52] OCTEAU, CLAUDIA. Local community participation in the establishment of national parks: planning for cooperation [D]. Vancouver: University of British Columbia, 1999.
[53] DAIM M S, BAKRI A F, KAMARUDIN H. Being neighbor to a national park: are we ready for community participation [J]. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2012, 36 (36):211-220.
[54] SIRIVONGS K, TSUCHIYA T. Relationship between local residents' perceptions, attitudes and participation towards national protected areas: a case study of Phou Khao Khouay National Protected Area, central Lao PDR [J]. Forest Policy & Economics, 2012, 21(1):92-100. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=baae70761339b1b5442e4c62ddc58690&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[55] SLADONJA B, POLJUHA D, FANUKO N. Introduction of participatory conservation in Croatia, residents' perceptions: a case study from the Istrian Peninsula [J].Environmental Management, 2012, 49:1115-1129. doi: 10.1007/s00267-012-9851-4
[56] FOCACCI M, FERRETTI F, MEO I D. Integrating stakeholders' preferences in participatory forest planning: a pairwise comparison approach from Southern Italy [J]. International Forestry Review, 2018, 19 (4):413-422. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=50209709038ba2ce3b8041208f543114&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[57] NIEDZIAŁKOWSKI K, KOMAR E, PIETRZYK-KASZYAŃSKA, et al. Discourses on public participation in protected areas governance: application of q methodology in Poland [J]. Ecological Economics, 2018, 145:401-409. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2017.11.018
[58] TWICHELL J, POLLNAC R, CHRISTIE P. Lessons from Philippines MPA management: social ecological interactions, participation, and MPA performance [J]. Environmental Management, 2018(2):1-12. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8784433186ab211c0d90f9908e50977e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[59] VODOUHÊ F G, COULIBALY O, ADÉGBIDI A, et al. Community perception of biodiversity conservation within protected areas in Benin [J].Forest Policy & Economics, 2010, 12(7):505-512. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=94446fccbe000eb608f79a06151c1f33
[60] RUIZMALLÉN I, NEWING H, PORTERBOLLAND L, et al. Cognisance, participation and protected areas in the Yucatan Peninsula [J]. Environmental Conservation, 2014, 41(3):265-275. doi: 10.1017/S0376892913000507
[61] RASOOLIMANESH S M, JAAFAR M, AHMAD A G. Community participation in world heritage site conservation and tourism development [J]. Tourism Management, 2017, 58:142-153. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2016.10.016
[62] IRVIN R A, STANSBURY J. Citizen participation in decision making: is it worth the effort [J]. Public Administration Review, 2010, 64(1):55-65. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/227541071_Citizen_Participation_in_Decision_Making_Is_It_Worth_the_Effort
[63] STEELMAN T A, ASCHER W. Public involvement methods in natural resource policy making: advantages, disadvantages and trade-offs [J]. Policy Sciences, 1997, 30(2):71-90. doi: 10.1023/A:1004246421974
[64] HÉRITIER S. Public participation and environmental management in mountain national parks [J]. Revue De Géographie Alpine, 2010, 98(1):610-612. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_3a11c02ff04b6e6da75aacd2b66c8590
[65] NIEDZIALKOWSKI K, PAAVOLA J, DRZEJEWSKA B. Participation and protected areas governance: the impact of changing influence of local authorities on the conservation of the Bialowieza Primeval Forest, Poland [J]. Ecology & Society, 2012, 17(1):1337-1347. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=79ce771d2d7c2fadeb7afa15a660a947&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[66] VOYER M, GLADSTONE W, GOODALL H. Methods of social assessment in Marine Protected Area planning: is public participation enough [J]. Marine Policy, 2012, 36(2):432-439. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2011.08.002
[67] DIETZ T, STERN P C. Science, values and biodiversity [J]. Bioscience.1998, 4(6):441-444. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xyyy201206160
[68] HOGG K, NOGUERA-MÉNDEZ P, SEMITIEL-GARCíA M, et al. Controversies over stakeholder participation in marine protected area (MPA) management: a case study of the Cabo de Palos-Islas Hormigas MPA [J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2017, 144(C):120-128. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1cdd880fec4013f043d81c99e9743b8b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[69] WEBLER T, TULER S, TANGUAY J. Competing perspectives on public[J]. Journal of Park and Recreation Administration, 2004, 22:91-113. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_0440dc454b52a8572f646454eafde7ec
[70] TULER S, WEBLER T. Public participation: relevance and application in the national park service [J]. Park Service, 2000, 20(1):24-26. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5399d4c627f0b9c2b2afb1cd9ea13a38&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[71] MANNIGEL E.Integrating parks and people: how does participation work in protected area management?[J]. Environmental Science & Policy, 2008, 5:498-511. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6b63d308e62b097051b344bd9697a29d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[72] Parksand Wildlife Commission of the Northern Territory. Public participation in protected area management[M]. Darwin:The Committee on National Parks and Protected Area Management, Benchmarking and Best Practice Program, 2002.
[73] SEWELL W R D, PHILLIPS S D. Models for the evaluation of public participation programmes [J].Natural Resources Journal, 1979, 19:337-358. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279574812_Models_for_evaluation_of_public_participation_programmes
[74] SANTANA-MEDINA N, FRANCO-MAASS S, SÁNCHEZ-VERA E. Participatory generation of sustainability indicators in a natural protected area of Mexico [J].Ecological Indicators, 2013, 25(1):1-9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d810fd897c7b929554a05ef333eadee7
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 张利,徐晓琰. 植物生物多样性受旅游业的影响与保护措施探析. 分子植物育种. 2023(20): 6922-6926 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈曦,梁松斌. 共同生产理论视角下生态系统服务级联框架的重构. 生态学报. 2023(20): 8268-8278 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张玉钧,熊文琪,谢冶凤. 提升游憩环境质量,建立国家公园公众参与行动框架. 旅游学刊. 2021(03): 7-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘道平,欧阳志云,张玉钧,邹红菲,钟林生,徐基良,曾江宁,金崑,钟永德,吴江洲,叶文,杨宇明. 中国自然保护地建设:机遇与挑战. 自然保护地. 2021(01): 1-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. WANG Jiaying. Research Progress of Public Participation in National Park Affairs in Foreign Countries Based on CiteSpace. Journal of Landscape Research. 2020(02): 119-122 .  必应学术
必应学术
6. 刘向南,刘天昊. 中国自然保护地体系建设现状、问题及对策研究. 农村经济与科技. 2020(11): 314-316 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 高情情,金光益,崔哲浩,张宏宇,吕弼顺. 东北虎豹国家公园入口社区生态旅游发展研究. 延边大学农学学报. 2020(02): 104-109 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)



 下载:
下载: