Evolution and Comparison of Government-led Governance Modes in Foreign Protected River Areas Based on the Concept of Adaptation
-
摘要: 河流保护地是维持河流突出价值的保护地专门类型,政府治理是河流保护地治理的主要模式。适应性旨在通过适应主体根据环境变化不断调整,减少不利影响,可为河流保护地政府治理提供思路和方法。基于适应性分析框架,从法律政策、治理主体、资源权属及资金来源4个方面,横向对比美国、新西兰、加拿大和澳大利亚4个国家的河流保护地政府治理模式及其演变过程,可得出如下结论:起源于美国的河流保护地在4个国家已经分别形成了4种不同的政府治理模式;联邦集权管理是美国联邦主导模式的突出特征,中央主导并适度分权是新西兰综合治理模式的表现形式,加拿大合作共管模式重视和尊重多方利益相关者,澳大利亚地方自治模式的管理权主要归属地方管理部门;适应所在国的自然保护地管理体制和政治制度差异是造成河流保护地政府治理模式变化的主要原因。未来中国河流保护地的建设必须基于适应性理念,根据国情和自然保护地体系的建设状况,在国家立法、分级管理、特许经营等方向积极探索。Abstract: Protected river area is a special type of protected area to maintain the outstanding value of rivers, and governance by government is the main mode of management for protected river area. Adaptation aims to reduce the adverse effects by adjusting the main body to environmental changes, which can provide ideas and methods for the management of protected river areas. Based on the adaptive analysis framework, this paper compares the mode of government-led governance and evolution process of protected river areas in the United States, New Zealand, Canada and Australia from four aspects: legal policies, governance bodies, resources ownership and funding sources. The following conclusions are drawn: four different modes of government-led governance have been formed in the four national protected river areas; federal centralized management is a prominent feature of the federal-led mode in the United States, central-led and moderate decentralization is the manifestation of the comprehensive governance mode in New Zealand, the cooperative co-management mode in Canada values and respects multiple stakeholders, and the management authority of the local self-government mode in Australia mainly belongs to the local management department. Adapting to the changes of the management system of natural protected area and political system in various countries is the reason for the difference in the mode of government-led governance of protected river areas. In the future, the construction of protected river areas in China must be based on the concept of adaptation, take into account the national conditions and the construction status of natural protected areas system, and the direction of national legislation, hierarchical management and franchising should be explored, so as to enrich and implement the planning of natural protected areas.
-
Keywords:
- protected river area (PRA) /
- government-led governance /
- governance mode /
- adaptation
-
自然保护地永续保护离不开有效的政府治理。世界自然保护联盟(International Union for Conservation of Nature,简称IUCN)及世界自然保护地委员会(World Commission on Protected Areas,简称WCPA)等认为“治理”关注的是决策主体、决策过程、决策主体的权责分担以及问责[1]。《保护地2018年度报告》(Protected Planet Report 2018)指出全球只有20%的保护地得到有效治理[2]。政府治理是自然保护地达到“善治”(Good Governance)的关键途径。
河流是自然保护地体系中重要的保护对象。河流作为一种自然要素,保护对象构成复杂多样,是水域、湿地及陆地的完整生态系统组合。同时,河流又是地球上所有生物群落和栖息地中受人类活动影响和威胁最大的区域[3]。20世纪50年代初,美国公众和政府开始认识到河流除了具有经济价值之外,还有生态价值和游憩价值,促进了河流保护的开始[4]。早期,美国政府主要通过利用国家公园、国家森林等其他类型保护地对河流实施保护,如黄石国家公园的黄石河、白河国家荒野保护区中的白河。在荒野思想和反坝运动的推动下,1968年美国国会正式通过了《荒野风景河流法案》(Wild and Scenic River Act,简称WSRA),标志着国家荒野风景河流体系(National Wild and Scenic River System,简称NWSRS)的正式建立。NWSRS的建立旨在保护和提高河流的自由流动性、水质以及杰出的显著性价值[5-6]。WSRA的通过是世界河流保护的分水岭,开启了通过自然保护地建设实现河流保护的新纪元。在NWSRS的影响下,1984年加拿大建立了加拿大遗产河流体系(Canada Heritage River System,简称CHRS),随后澳大利亚和新西兰也建立了自己的河流保护地体系(Protected River Area System,简称PRAS)对河流进行保护[7]。
迄今,作为淡水保护地的一种类型,河流保护地并没有统一的定义。参考IUCN的自然保护地概念,将河流保护地(Protected River Area,简称PRA)定义为:用来保护并维持河流自然价值和生态健康,通过法律或其他有效方式获得认可并进行管理的内陆水域。美、加等国的河流保护地系统在保护河流、湖泊等内陆水域中发挥了较好的作用,已成为国家重要的自然保护地类型之一。目前,关于河流保护地体系治理的研究,主要集中在法律体系、管理机制、保护规划和社区参与等方面[8-11],不同国家河流保护地治理模式的比较及其形成原因鲜有人研究。
治理模式在河流保护地实现保护目标方面具有关键作用。治理模式决定了相关的成本收益分担,是预防和化解社会冲突的关键,影响着社会、政治和财政支持[12]。目前,全球自然保护地治理模式大都以政府治理为主,但环境的变化对传统的政府治理模式提出了新要求和挑战。适应性[13-15]理念作为保护地政府治理模式创新的指导思想,对保护地建设具有重要意义。河流保护地体系作为一种保护地制度体系,需要根据国情差异和河流特点形成符合自身的治理模式。为此,本研究基于适应性理论框架,针对已经建立河流保护地的美、加、澳、新4个国家,比较其河流保护地治理模式的差异,并剖析造成差异的原因,进而为中国自然保护地体系和河流保护地的未来建设提供借鉴。
一. 适应性研究框架
一 概 念
适应性是应对环境复杂性、不确定性及变化的选择。适应性原指若一个物种在不同的环境下仍能保持自身的存在,则其具有适应性[16-17]。自然选择是适应的发生和维持唯一可接受的解释[18]。社会系统表现出的适应性与自然系统类似[19],Steward[20]首次提出了“文化适应”概念,用于描述“文化核心”(即区域社会)调整自身行为适应自然环境的过程,突破了适应性自然科学的范畴。后来,适应性被广泛应用于全球变化、可持续发展等新领域,脆弱性、恢复力等成为适应性研究的核心概念[21]。IPCC(Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change,政府间气候变化专门委员会)指出应对全球气候变化的适应性是通过调整系统进而降低脆弱性或增强弹性的过程来体现的[22]。社会−生态系统(Social-Ecological Systems)是一种复杂适应系统,有学者用“适应性”来概述适应主体及其环境间的非线性和相互作用,促进可持续发展[23]。WANG等[24]和SMIT等[25]认为适应性是适应主体的行为特征,强调主体在“干中学”,以趋利避害,增强恢复力。目前,适应性已是全球变化科学的核心概念之一[26],也是可持续发展研究的关键要素和分析框架[27]。
适应性概念从自然科学到社会科学一直处于动态发展过程,是一个复杂的过程,包含了学习、调整、响应等环节。保护地政府治理的适应性是适应主体为减少对保护地的负面影响,调整其行为和系统结构的过程,以实现系统动态平衡。
二 框架构成
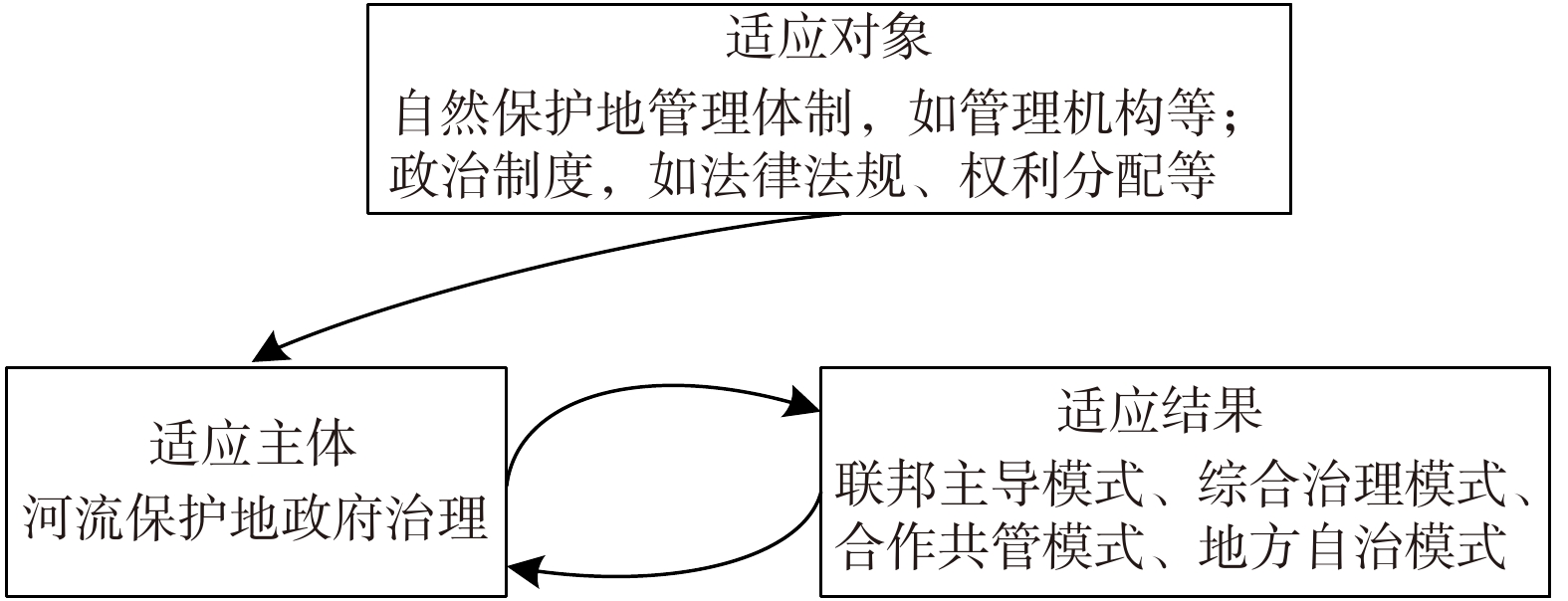
“适应性”既指适应的过程,也指适应的条件,在特定的学科中有更具体的解释。适应性框架需基于三个问题[28-29]:适应什么?谁或什么适应?适应是如何发生的?任何对适应性的科学分析都需要明确这三个要素。
1)适应对象。任何对适应系统性的分析都需明确“适应什么”,即适应的对象。不同的适应过程,适应对象亦不同,可以是生物等实体,也可以是时间、空间范围、现象问题等非实体,如包含气候变化的自然生态系统问题、环境难民问题都可以视为是全球变化背景下的适应对象。分析适应对象的特性,有利于适应主体做出调整。
2)适应主体。适应主体是适应的关键要素,任何适应性的研究都需要对系统的主体进行定义或描述。适应主体既与尺度规模相关,如国家、区域等,也与系统的性质有关[30],如生态、经济、社会、政治等。社会−生态系统的适应主体是其系统组分,既包含人类社会也有自然系统。
3)适应过程和结果。适应过程和由此产生的适应结果回答了“适应如何发生”的问题。适应的过程和形式依据不同属性可划分为不同的类型,例如,有学者将适应分为长期的和短期的,也有学者认为在没有管理的自然系统中,适应是自发的,而公共机构发起的适应通常是有计划的并可能是预期的[28]。根据内外部因素和适应主体的适应能力动态变化,HOLLING等[31]提出适应性循环(adaptive cycle)模型,表明这种过程是不断循环的,适应结果是评价适应是否成功的依据。
适应主体和适应对象之间存在不同,都会引起适应过程和结果的差异。在不同国家,保护地政府治理的适应结果直接表现为不同的治理模式。
二. 河流保护地政府治理模式比较
依据政府治理的主体(主要行为者)对保护地管理所负有的权力和责任的不同,可将河流保护地政府治理模式分为4种类型[12]。
一 联邦主导模式
联邦主导模式是以联邦政府为主导,联邦机构享有决策权,承担责任和义务,具有强执行力和高效性的特征[32],美国的NWSRS政府治理是其中的典型代表。截至2019年4月,美国的国家荒野风景河流单元数量已达226段(一条河流可能只有一段或多段符合要求,故其数量单位用段),长度为21 585.3 km[33],已经成为联邦层面重要的保护地类型之一。NWSRS的法律体系构成以联邦立法为主,并辅以相关的环境保护法案[34]。WSRA明确了国家荒野风景河流的地位、目的、遴选标准和管理过程等各项事宜以及具体的技术性管理;同时,辅之以一系列配套的计划、政策、战略、指南等。此外,国家荒野风景河流保护也需遵循水资源和野生动物保护等方面的法律,使得河流保护地体系建设的各项运作有法可依、有章可循。NWSRS的治理主体以联邦机构为主,非联邦机构为辅。联邦机构包括林务局、国家公园管理局、野生生物与鱼类管理局、土地管理局[35]等,非联邦机构主要涉及州政府或地方政府。这种联邦与非联邦治理机构形成了4种组合管理方式:单一联邦机构进行统一管理;不同联邦机构进行联合管理;州或地方政府进行地方管理;“联邦−州−地方政府”进行合作管理[36]。资源权属方面,NWSRS赋予联邦机构绝对的管理权。大部分荒野风景河流土地属于联邦,对于非联邦所有的土地和水资源,WSRA明确规定联邦机构拥有优先获得权、购买权及限制权,从而控制河流及其沿岸土地的使用方式。一部分私人土地通过地役权(Easement)方式加以保护,一部分私人土地和水资源则通过劝说、环境教育等方式进行管理,让原所有者自觉参与到河流保护行列之中[34]。国家荒野风景河流治理的资金保障有多种渠道,主要是联邦和地方财政支持,其他还有特许经营收入、企业赞助、非政府组织资助等形式,丰富多样的资金渠道为荒野风景河流体系的发展提供了有力保障。
二 综合治理模式
综合治理模式是由联邦政府主导治理方向并适度分权,将部分管理权下放至地方政府,既有联邦政府的主导,又有地方政府的自主决策,新西兰的荒野风景河流体系是典型代表。新西兰是一个深受河流影响的国家,河流是重要的景观特征并塑造着国家环境[37]。1981年,《水土保持法修正案》(Water and Soil Conservation Amendment Act)的通过标志着荒野风景河流体系的正式形成,它首次提出保护河流突出的荒野、风景、娱乐或其他自然特征。
荒野风景河流的保护法律由中央政府制定。新西兰《水土保持法修正案》(也被称为《野生和风景河流法》)的颁布催生了水保护令(Water Conservation Orders,简称WCOs)。1991年通过的《资源管理法》(Resource Management Act,简称RMA),为管理河流和河流内的水体提供了主要的立法保障,专门承认和保护河流水体价值的WCOs被纳入。由于过度复杂的申请程序,目前WCOs仅覆盖了新西兰13条河流的部分河段和2个湖泊,发展较为缓慢[37]。此外,《国家公园法案》(National Parks Act)(1980)、《保护法》(Conservation Act)(1987)、1983年淡水渔业条例等也为荒野风景河流的保护提供了支持。
新西兰未成立管理河流保护地的专门机构。根据《保护法》和RMA,保护部、渔猎委员会和区域委员会是河流管理的主要机构,职责包括管理保护区和野生动物,开展淡水渔业研究,倡导保护水生生物和淡水等。同时,区域委员会在水污染防治、水资源利用以及沿河土地使用方面起着重要作用。
新西兰土地所有权分为政府所有、私人所有和租借持有3种形式。所有的土地管理权都集中在中央政府,存在部分公有土地的所有权与管理权分离。对于私人土地,政府需要购买或同私人达成协议后进行联合管理。WCOs仅保护河道水流,并不像美国一样对河流周边土地也进行保护。当出现资源权属冲突时,由地区或市议会审议对影响水资源的土地使用进行决策。
河流保护地的保护资金近90%来源于中央财政,各种其他基金也是来源之一,如自然遗产基金等。
三 合作共管模式
合作共管模式是一种多主体参与的模式,重视利益相关者的参与、互动和共识达成,遵循约束、协调和控制的管治特征,加拿大CHRS是合作共管模式的典范。加拿大国土广阔,有着众多价值突出的河流或航道,1984年各级政府联合成立了国家河流保护项目−CHRS。政府与当地社区和管理团体合作,在全国范围内遴选优秀遗产河流,并鼓励对这些河流进行长期管理以保护其自然、文化和游憩价值,使加拿大人代内、代际都能受益[38]。截至2017年底,CHRS已经提名42条遗产河流,其中39条已指定保护,总长近12 000 km[39]。
CHRS作为一个国家项目,只是一个公共信托,这就决定了其本身没有立法权。《遗产河流系统:政策、程序和操作指南》是加拿大遗产河流项目的基础文件。该文件详细界定了CHRS的总体原则、治理结构、提名和指定过程以及监测制度,成为联邦、省和地区管辖范围内参与该项目的关键文件,包含指导CHRS项目的《遗产河流宪章》以及十年战略计划等内容。同时CHRS在具体实施时有相应的配套政策,如国家公园指导原则和运营政策中的遗产河流政策[40]等内容。
与美国NWSRS不同,CHRS由遗产河流委员会(Heritage Rivers Board,简称HRB)进行管理。HRB由联邦、省、地区政府的官员组成,由公园管理局、印第安事务及北方发展部代表联邦政府[41],普通民众可由政府指派进入HRB来参与管理。合作共管模式的思想是坚持民主平等原则,参与主体有政府部门、当地居民、学者和非政府组织,如Three River由三河协会进行管理,Hillsborough河由私人土地所有者进行管理。
依据《遗产河流宪章》,各个区域和流域的管理机构自愿加入河流保护项目,被纳入项目的遗产河流,其资源权属不改变。CHRS尊重土著社区、土地所有者和个人权利,参与者保留在CHRS中河流的管辖权力,其中包括土地所有权、被提名的河流的确定及按照该系统目标运营和管理的权利。
联邦资金是CHRS运行的资金来源,主要由国家公园管理局提供。作为项目的牵头机构,国家公园管理局通过其秘书处,为编制文件和与CHRS有关的研究和项目提供财政和技术援助,以完成提名和指定遗产河流的研究和计划[42]。
四 地方自治模式
地方自治模式的鲜明特征是保护地的管治权归属地方政府,联邦政府主要负责对外沟通交流及内部引导协调,保留外交权和调处权,澳大利亚河流保护地治理体系是其中的代表。1979年,荒野协会及其他环保组织在塔斯马尼亚州反坝运动中的成功,标志着澳大利亚河流保护意识上升到国家层面[43]。1993年,澳大利亚遗产委员会启动“荒野河流项目”,系统识别澳大利亚的野生河流,制定可持续管理野生河流的准则[44],以提高人们对野生河流价值的认识,保护真正意义上的荒野河流。具体落实河流保护概念的是各州及领地,且采取的形式极为不同,如昆士兰州、新南威尔士州的“荒野河流”、维多利亚州的“遗产河流”[45]。
各州政府的专项法规或条例是平行而非隶属关系。荒野河流项目结束之后,2005年昆士兰州政府为履行承诺提出了“荒野河流法”(Wild Rivers Act,简称WRA)(2014年废除),成为澳大利亚第一个立法保护野生河流的地区,并在2007—2010 年间提名了13条野生河流[46]。WRA作为河流保护的管理依据,与可持续规划法案、水资源法案及其他相关法律协同运作,为保护荒野河流价值可持续发展奠定了基础[43]。此后,其他各州也相继出台荒野河流(遗产河流)的法规和政策,如维多利亚州的《遗产河流法》、西澳大利亚州的《河流恢复手册》、首都领地的《水资源法》等。
荒野河流的治理主体以地方政府为主,联邦政府为辅。地方管理部门对当地河流保护地的立法、规划、决策和执行拥有自主权,联邦政府对内与各地方政府和区域资源管理规划机构合作,对外履行国际条约义务[8]。具体的管理机构因州而异,如维多利亚州的可持续发展与环境部、西澳大利亚州的水资源与环境规划局、首都领地的环保局。对跨界河流,相关州联合设立区域管理委员会,以实现对河流的整体保护,如墨累达令流域委员会、昆士兰州和新南威尔士州边界河流委员会。各州因地制宜实行多样化管理,不仅增加了河流保护地管理的灵活度,也相互提供了经验借鉴。
澳大利亚有约13%的荒野河流处于自然保护区内,超过1/3位于私人土地上[44]。当河流保护剥夺了原住民传统的土地权利时,由地方政府进行协商。例如,昆士兰州的WRA在原住民土地权属问题上与《原住民土地权法》存在矛盾,受到反对派Abbott和著名土著活动家Pearson的强烈反对,WRA在争议声中艰难推行,直到反对派竞选成功,《区域规划利益法》取代了约克角半岛的WRA,才平息了荒野河流保护和原住民之间土地权的纠纷。
保护荒野河流的资金主要由联邦政府提供。随着原住民在保护区内自然和文化资源保护中重要性的凸显,对处于原住民土地上的荒野河流,联邦政府在原住民自愿的前提下为其提供资金和技术支持[47]。同时,联邦政府鼓励私人参与保护,增加了资金来源。
三. 河流保护地适应性政府治理模式形成原因
美国NWSRS作为河流保护地体系的“原种”,形成了一套联邦主导的政府治理模式,其政府治理理念逐步向全球传播。各国在自身实践过程中,结合国情演化出不同形式的“变种”,形成了与国情相适应的治理模式,这是政府治理差异化,也是适应性治理的表征。4种河流保护地治理模式对比结果如表1所示,4种模式在法律机制、管理机构、资源权属3个方面表现出较大差异,资金来源均是多元化的资金渠道,国家财政拨款在支持河流保护地建立与管理过程中承担主要责任,特许经营收入、非政府组织及企业等社会团体捐助也提供了支持。结合上述研究表明,各国PRAS政府治理模式是适应主体,适应对象是各国保护地管理体制和政治制度,4种治理模式是适应的结果。
表 1 美、加、澳、新4国河流保护地政府治理模式比较美国 新西兰 加拿大 澳大利亚 建立时间 1968年 1981年 1984年 1993年 保护重点 河流杰出价值 突出荒野、风景的水体 河流遗产价值 荒野河流价值 治理模式 联邦主导型 综合治理型 合作共管型 地方自治型 法律体系 联邦专项性法律 联邦指导性法规 专项性政策 地方性法规 管理机构 联邦与非联邦治理机构 中央−地方部门 公共信托 因州而异的地方机构 资源权属 联邦政府为主 中央−地方合作管理 多方合作 地方政府为主 资金来源 多元化 一 不同治理模式是适应保护地管理体制差异的结果
4种河流保护地体系与自然保护地体系存在被包含或部分被包含的关系,治理模式深受所在国自然保护地管理体制影响,主要是通过不同的管理机构作用于适应主体,从而形成4种适应过程和结果。
美国NWSRS是国家保护地体系的有机组成部分,林务局、国家公园管理局等联邦机构是其主要的治理机构,延续了保护地联邦主导治理模式。美国大多数自然保护地都是采取政府治理模式,主要特征是联邦集权、垂直管理,国家公园、国家森林等“完全中央集权”。当保护地治理体系的治理客体变成构成复杂的河流时,其政府治理模式适应性地变成了局部“非完全中央集权”的联邦主导形式[34],主要体现在两个方面,一是治理主体的多元化,荒野风景河流治理主体除联邦机构外还包括当地政府、协调管理委员会及公众;二是资源权属的多样,荒野风景河流资源包括土地和水资源,其所有权和管理权是分开的。
新西兰荒野风景河流治理模式沿袭了联邦政府主管、地方政府辅助的形式。目前,新西兰保护地管理体系中,政府机构和非政府组织是管理主体。政府机构由保护部和其他一些部门组成,是保护地体系的中心管理机构。保护部拥有保护地的土地所有权和管理权,签署执行相关法律法案(包括认可毛利人参与保护的地位的相关法规),同时其设有11个区域办公室,各级区域管理机构负责各自区域的管理规划编制[48]。保护地的资金保障主要来源于政府财政,其他来源包括基金项目和旅游收入等[49]。正是对保护地管理体制的充分适应,才形成保护部和地方机构主管河流保护地的综合治理模式。
加拿大近一半的遗产河流位于国家公园内,国家公园管理局是CHRS项目的牵头机构,是自然保护地的重要组成,河流保护地治理模式是国家自然保护地管理体制的延伸。加拿大自然保护区的建立并不是通过立法来明确界定的[50],95%的自然保护区由政府管理,伙伴协作、共同保护是其突出的管理理念,如国家公园的建设与管理主体包括政府、企业、学术界、非政府组织和私人管理者等。包含大量政策、指南等的指导文件,多方构成的治理主体,尊重各方权益的资源权属及政府财政为主的资金保障,是河流保护适应自然保护管理体制的有力证据。
相比美加两国,澳大利亚河流保护地体系更为独立,虽未完全纳入联邦保护地体系,但作为自然保护地的一类,河流保护地治理模式大体遵循原有保护地管理体制。各州、领地是自然保护地发展的主导者,保护地的管理主体是各州、领地政府机构[51]。20世纪70年代《国家公园和野生动植物保护法案》颁布后,联邦政府才开始在管理上担任实质性角色,负责国家层面的保护区并起协调作用。2008年,联邦政府将国家保护地体系列为其6 大优先事项之一并提供资金,也包括对土著保护地的资金支持[52]。联邦政府和州、领地政府分别制定相应的法律对各自负责的保护地实行保护,河流保护地基于自然保护地的地方管理体制做出响应,形成地方自治模式。
二 不同治理模式也是适应国家政治制度差异的结果
不同的政治环境和体制是4国形成河流保护地适应性政府治理模式的基石。美国、加拿大、澳大利亚同属联邦制国家,三权分立却不尽相同;新西兰实行君主立宪制混合英国式议会民主制。适应主体受到各国的法律法规、权利分配等的扰动而出现不同的适应结果。
美国联邦起主导作用的政治制度是其河流保护地治理模式关键的适应对象。美国联邦宪法发展过程呈现出联邦权力扩大和加强的趋势[53],联邦政府集权是保护地联邦主导的政府治理模式形成的重要原因[54]。联邦政府与州政府的权威分配依照宪法规定的原则进行,联邦政府地位高于州政府,州政府分权在中央集权基础上进行[55]。即便大部分土地为私人所有,但美国政府可以通过购买、租赁、税收等方式获得其所有权,保护地所有权主要为联邦政府拥有[56]。联邦政府机构是自然保护地的主导者,河流保护地体系政府治理为联邦主导模式顺理成章。
集中的政治制度是新西兰河流保护地政府治理适应性模式出现的刺激因素。新西兰是具有议会制政府的君主立宪制国家,相较于美、加、澳,政治制度较为简单,权利分布在议会(由君主和众议院组成)、行政和司法三个政府部门,议会是只有众议院的“一院制”,对行政权力的制约不大,内阁通过简单多数的投票制实现对立法机关的控制[57]。新西兰没有成文的宪法或高于议会通过的法律的任何形式的法律,中央与地方的垂直关系较为明显,单一集中的政治制度为保护地中央政府主管和立法提供了条件,是河流保护地中央与地方联合治理的适应结果形成的关键。
加拿大独特的联邦制作为适应对象,塑造了河流保护地合作共管的政府治理模式。加拿大采取联邦和各省之间分权的联邦体制,省政府拥有更彻底的分权,省政府是政府体系的主角,在各自的管辖范围内拥有强大的自主权和立法权。1867年宪法规定了联邦与各省的立法权,联邦权力集中于国防、外交、货币及省级贸易等全国性事务上,各省立法主要在省内事务方面,如自然资源、教育和健康等[58]。联邦政府无权直接管理各省的土地资源,但联邦政府与地方政府之间具有较强的协作性[59]。以上各种因素导致了保护地政府管理和伙伴协作机制,出现由国家公园管理局牵头、多方参与的治理模式。
澳大利亚河流保护地地方自治模式的形成归因于其“联邦弱、地方强”的政治制度。各州原为英属殖民地,1900年各个殖民地联合通过《澳大利亚联邦宪法》,并于第二年宣布成立澳大利亚联邦。但联邦政府与州政府之间的协作不如加拿大成熟。联邦建立初期,州政府的权力大于联邦政府,联邦政府在某些方面甚至缺少干预权;随着国家的发展,联邦政府逐渐成为主要角色,但各州独立性依旧,有各自的宪法和独立的政治体制,联邦政府主要起协调和引导作用,是典型的“弱联邦−强地方”制度,联邦与各州互相牵制。澳大利亚保护地治理随本国政治制度的发展而发展,河流保护地主要由各州政府负责相关事项,适应形成了地方自治的治理模式。
四. 结 语
综上所述,各国河流保护地政府治理模式各具优缺点。美国联邦主导的河流保护地政府治理推行了有效的分级管理,联邦和地方各有侧重,管理方式多元化,法律制度完善,实施性强;新西兰综合治理模式虽严格地保护了河流,但公众参与度不高;加拿大合作共管模式充分调动了各种保护力量,但专项法律的缺位和自愿参与的原则削弱了对河流的保护强度;澳大利亚地方自治模式自由度高,但缺少联邦层面法律引领约束,造成河流保护进程坎坷。
适应性是保护地治理的必然选择。自然保护地治理没有统一的模式,必须依据不同的治理环境进行设计[60],河流保护地体系也不例外。以上研究表明,各国有本土化的法律政策和管理机构,河流保护地体系体现出适应性特征。从主体、对象和过程[29]三个要素来看,适应性是河流保护地政府治理适应不同治理环境的结果,其深层原因则是适应所在国政治制度的变化(见图1)。
中国目前还没有自己的河流保护地,与国外河流保护地最接近的是国家水利风景区。但是,国家水利风景区与河流保护地相比,在法律、管理机构等方面仍有较大差距。2018年习近平总书记指出,“长江拥有独特的生态系统,要把修复长江生态环境摆在压倒性位置”,2020年中央又提出了“黄河流域大保护、大治理”,表明我国河流保护意识得到进一步加强,河流管理将由单一管理转变为综合治理,专门的河流保护地类型将成为一种潜在选择。2020年12月,中国第一部有关流域保护的专门法律−《长江保护法》出台,《黄河保护法》也在起草之中,预示着专门的河流保护地体系及其相关法律极有可能在中国诞生。
河流是一种独特的生态系统和地理单元,建立中国的河流保护地体系应该是中国特色自然保护地体系新的拓展和努力方向。根据适应性原理和方法,汲取4国河流保护地建设的成功经验,相关部门应在法律、机构、社区等方面予以提前考虑,为探索出符合中国国情的河流保护地政府治理模式奠定基础。要以《长江保护法》《黄河保护法》的出台为契机,建立国家层面的专门法律,作为统领河流保护地发展的指南和建设的依据。同时要以生态文明思想为指导,兼顾生态环境保护和利用。由于国情不同,中国难以像某些发达国家一样采取拆坝等方式来保护荒野河流,但是我们可以保护人民身边的河流,打造城乡健康美丽河流。
综观国外河流保护地管理机构,并结合中国现有政治制度,中国河流保护地体系建设需要由一个部门进行统筹,实行分级管理,采取中央直接管理、中央委托地方政府管理、中央和地方政府共同管理等模式[61],同时建立企业、社会组织和公众参与的长效机制。我国土地和河流等自然资源都属于公有,不存在河流保护地建设与私人土地、河湖资源之间的权属冲突,但是,中国存在土地集体所有的居民生计依赖与全民生态保护责任的使用限制之间的矛盾。基于此,应探索河流保护地资产使用权的多样化,在不损害河流生命体和生态系统的前提下,完善使用权转让、出租、作价出资(入股)等权能,探索与河流相关的特许经营活动,鼓励原住民共参共享。国内外自然保护地的资金来源基本是以财政投入为主,并鼓励非政府组织和个人提供支持,河流保护地建设也是如此。我国今后在建立多种资金来源机制之外,还要实现与河流保护地相关生态产品的货币化,明晰河流生态产品数量及质量,通过市场机制,实现绿水青山向金山银山的转换,进一步反哺到河流保护地的运营管理。
-
表 1 美、加、澳、新4国河流保护地政府治理模式比较
美国 新西兰 加拿大 澳大利亚 建立时间 1968年 1981年 1984年 1993年 保护重点 河流杰出价值 突出荒野、风景的水体 河流遗产价值 荒野河流价值 治理模式 联邦主导型 综合治理型 合作共管型 地方自治型 法律体系 联邦专项性法律 联邦指导性法规 专项性政策 地方性法规 管理机构 联邦与非联邦治理机构 中央−地方部门 公共信托 因州而异的地方机构 资源权属 联邦政府为主 中央−地方合作管理 多方合作 地方政府为主 资金来源 多元化 -
[1] 解钰茜,曾维华,马冰然. 基于社会网络分析的全球自然保护地治理模式研究[J]. 生态学报,2019,39(4):1394-1406. [2] UNEP-WCMC, IUCN, NGS. Protected planet report 2018[M]. Cambridge, Gland, Washington D.C.: UNEP-WCMC, IUCN, NGS, 2018.
[3] MADSEN K, RAFFAN J. Wild rivers, wild lands[M]. Toronto, Ontario: Lost Moose, the Yukon Publishers, 1997.
[4] 李鹏,张端,戴向前,等. 美国荒野风景河流体系发展阶段及其主要影响因素[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2018,16(6):178-186. [5] BORRINI G, KOTHARI A, OVIEDO G. Indigenous and local communities and protected areas: towards equity and enhanced conservation: guidance on policy and practice for co-managed protected areas and community conserved areas[M]. Gland, Cambridge: IUCN, 2004.
[6] TARLOCK A D,TIPPY R. Wild and scenic rivers act of 1968[J]. Cornell L Rev,1970,55(5):707-739.
[7] CARVER S. The river wild:towards a global assessment of wild rivers[J]. International Journal of Wilderness,2018,24(1):1-13.
[8] HUGHEY K F,RENNIE H G,WILLIAMS N J. New Zealand's 'wild and scenic rivers':geographical aspects of 30 years of water conservation orders[J]. New Zealand Geographer,2014,70(1):22-32. doi: 10.1111/nzg.12037
[9] SLATER L. 'Wild rivers,wild ideas':emerging political ecologies of Cape York wild rivers[J]. Environment and Planning D:Society and Space,2013,31(5):763-778. doi: 10.1068/d3012
[10] SMITH J W,MOORE R L. Perceptions of community benefits from two wild and scenic rivers[J]. Environmental Management,2011,47(5):814-827. doi: 10.1007/s00267-011-9671-y
[11] 朱春全, 欧阳志云. IUCN自然保护地管理分类应用指南[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2016. [12] BORRINI G, DUDLEY N, JAEGER T, et al. Governance of protected areas: from understanding to action[M]. Gland: IUCN, 2013.
[13] GROSS J, WATSON J, WOODLEY S, et al. Responding to climate change: guidance for protected area managers and planners[M]. Gland: IUCN, 2015.
[14] 李婧,韩锋. 自然保护地社区适应性协同管理路径研究与启示[J]. 绿色科技,2020(10):172-175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9944.2020.10.058 [15] 王文杰,潘英姿,王明翠,等. 区域生态系统适应性管理概念、理论框架及其应用研究[J]. 中国环境监测,2007,23(2):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2007.02.001 [16] BUTZER K W. Adaptation to global environmental change[J]. Professional Geographer,1980,32(3):269-278. doi: 10.1111/j.0033-0124.1980.00269.x
[17] FUTUYMA D. Evolutionary biology[M]. Sunderland, Mass: Sinauer Associates, 1979.
[18] WILLIAMS G C. Adaptation and natural selection: a critique of some current evolutionary thought[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2018.
[19] GALLOPIN G,GUTMAN P,MALETTA H. Global impoverishment,sustainable development and the environment:a conceptual approach[J]. International Social Science Journal,1989,41(3):375-397.
[20] STEWARD J H. Theory of culture change: the methodology of multilinear evolution[M]. Illinois: University of Illinois Press, 1972.
[21] 尹莎,杨新军,陈佳. 人地系统适应性研究进展:概念,理论框架与方法[J]. 地理科学进展,2021,40(2):330-342. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.02.013 [22] 崔胜辉,李旋旗,李扬,等. 全球变化背景下的适应性研究综述[J]. 地理科学进展,2011,30(9):1088-1098. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2011.09.003 [23] 范冬萍,何德贵. 基于CAS理论的社会生态系统适应性治理进路分析[J]. 学术研究,2018(12):6-11,177. [24] WANG A D,SHARP N P,AGRAWAL A F. Sensitivity of the distribution of mutational fitness effects to environment,genetic background,and adaptedness:a case study with Drosophila[J]. Evolution,2014,68(3):840-853. doi: 10.1111/evo.12309
[25] SMIT B,WANDEL J. Adaptation,adaptive capacity and vulnerability[J]. Global Environmental Change,2006,16(3):282-292. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2006.03.008
[26] 陈宜瑜. 对开展全球变化区域适应研究的几点看法[J]. 地球科学进展,2004,19(4):495-499. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.04.001 [27] 仇方道,佟连军,姜萌. 东北地区矿业城市产业生态系统适应性评价[J]. 地理研究,2011,30(2):243-255. [28] PELLING M. Adaptation to climate change: from resilience to transformation[M]. USA and Canada: Routledge, 2011.
[29] SMIT B,BURTON I,KLEIN R J,et al. The science of adaptation:a framework for assessment[J]. Mitigation and adaptation strategies for global change,1999,4(3):199-213.
[30] SMIT B, BURTON I, KLEIN R J, et al. An anatomy of adaptation to climate change and variability[M]//SMIT B, BURTON I, KLEIN R J, et al. Societal adaptation to climate variability and change. Dordrecht: Springer, 2000: 223-251.
[31] HOLLING C S, GUNDERSON L H. Panarchy: understanding transformations in human and natural systems[M]. Washington, DC: Island Press, 2002.
[32] KLOS T B,NOOTEBOOM B. Adaptive governance:the role of loyalty[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes,1998,31(16):111-116. doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)40467-8
[33] River mileage classifications for components of the national wild and scenic rivers system. [EB/OL].[2021-02-28]. https://www.rivers.gov/documents/rivers-table.pdf.
[34] 李鹏,张端,赵敏,等. 自然保护地非完全中央集权政府治理模式研究−以美国荒野风景河流体系为例[J]. 北京林业大学学报(社会科学版),2019,18(1):60-69. [35] DIEDRICH J.Wild & scenic river management responsibilities[R]. Portland: Technical Report of the Interagency Wild and Scenic Rivers Coordinating Council, 2002.
[36] BROUGHER C.The wild and scenic rivers act and federal water rights[R]. Lincoln: Congressional Research Service, 2008.
[37] AUTHORITY N Z C. Protecting New Zealand's rivers[M]. Wellington: New Zealand Conservation Authority, 2011.
[38] Canadian heritage rivers system strategic plan 2008-2018 [EB/OL]. [2021-02-28]. https://chrs.ca/en/strategic-plan-2008-2018.
[39] Principles, procedures and operational guidelines(PPOG) [EB/OL]. [2021-02-28]. https://chrs.ca/en/resources/principles-procedures-and-operational-guidelines-ppog.
[40] Parks Canada guiding principles and operational policies: part II - activity policies: Canadian heritage rivers policy [EB/OL].(2017-03-30)[2021-02-28]. https://www.pc.gc.ca/en/docs/pc/poli/princip/sec2/part2c.
[41] Canadian heritage rivers policy-background [EB/OL].(2017-06-12)[2021-02-28]. https://www.pc.gc.ca/en/docs/pc/poli/princip/sec2/part2c/part2c1.
[42] Canadian heritage rivers policy- technical and financial assistance [EB/OL].(2017-06-12)[2021-02-28]. https://www.pc.gc.ca/en/docs/pc/poli/princip/sec2/part2c/part2c5.
[43] DIXON N. A framework to protect wild rivers in Queensland: the Wild Rivers Bill 2005(Qld)[M]. Queensland: Queensland Parliamentary Library, Research Publications and Resources Section, 2005.
[44] STEIN J,STEIN J,NIX H. Wild rivers in Australia[J]. International Journal of Wilderness,2001,7(1):20-24.
[45] KINGSFORD R T,NEVILL J. Scientists urge expansion of freshwater protected areas[J]. Ecological Management & Restoration,2005,6(3):161-162.
[46] 周语夏,刘海龙. 国际自然流淌河流保护的政策工具与成效比较[J]. 风景园林,2020,27(8):42-48. [47] CORBETT T, CLIFFORD C, LANE M B. Achieving indigenous involvement in management of protected areas: lessons from recent Australian experience[M]. Queensland: Centre for Australian Public Sector Management, Griffith University, 1998.
[48] 赵智聪,庄优波. 新西兰保护地规划体系评述[J]. 中国园林,2013,29(9):25-29. [49] 王金凤,刘永,郭怀成,等. 新西兰自然保护区管理及其对中国的启示[J]. 环境保护,2006(5):75-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9705.2006.05.021 [50] 王晓丽. 中国和加拿大自然保护区管理制度比较研究[J]. 世界环境,2004(1):31-36. [51] 温战强,高尚仁,郑光美. 澳大利亚保护地管理及其对中国的启示[J]. 林业资源管理,2008(6):117-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6622.2008.06.025 [52] 秦天宝. 澳大利亚保护地法律与实践述评[C]//中国法学会环境资源法学研究会. 生态文明与环境资源法: 2009 年全国环境资源法学研讨会(年会)论文集.昆明: 昆明理工大学,2009: 550-555. [53] 周林刚. 从基本权利的角度解释美国的联邦集权[J]. 学术月刊,2017,49(1):86-91. [54] 董礼胜,曹冬英. 美国“分权-集权”钟摆运动研究[J]. 中共福建省委党校学报,2017(2):48-58. [55] 林尚立. 国内政府间关系[M]. 杭州: 浙江人民出版社, 1998. [56] 周奥,王瑗玲,廖蓉. 美国联邦保护地的保护措施[J]. 中国土地,2018(4):32-34. [57] Our system of government [EB/OL].(2013-05-01)[2021-02-28]. https://www.parliament.nz/en/visit-and-learn/how-parliament-works/our-system-of-government/.
[58] 何晓琦. 加拿大联邦主义视野下的立法权分配和宪法司法审查[J]. 法制与社会,2020(5):5-7,30. [59] 杨雅琴. 我国政府间事权与支出责任划分再思考−基于对加拿大财政联邦主义制度安排的分析[J]. 地方财政研究,2015(5):34-39. [60] EAGLES P F. Governance models for parks, recreation and tourism[M]//HANNA K S, CLARK D A , SLOCOMBE D S. Transforming parks and protected areas: policy and governance in a changing world. London: Routledge, 2008: 39-61.
[61] 唐芳林. 中国特色国家公园体制建设的特征和路径[J]. 北京林业大学学报(社会科学版),2020,19(2):33-39. -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 袁加华. 隆化某矿区复垦土地再利用适宜性分析. 现代矿业. 2024(01): 239-242 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 莫俊杰,胡靖,田世政. 基于“四体”理论的漂流游憩研究综述与启示——以国际英文期刊文献为例. 中国生态旅游. 2023(04): 649-664 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: